 Odds are that, if you’re a flooring contractor or inspector, you’re already familiar with the ASTM-F-2170 standard for measuring moisture in concrete. This testing method for concrete has been the industry standard for years now, allowing flooring specialists to establish whether or not concrete subfloors are ready to be built on, or a coating or sealer to be applied.
Odds are that, if you’re a flooring contractor or inspector, you’re already familiar with the ASTM-F-2170 standard for measuring moisture in concrete. This testing method for concrete has been the industry standard for years now, allowing flooring specialists to establish whether or not concrete subfloors are ready to be built on, or a coating or sealer to be applied.
However, most laymen have never even heard of the standard, let alone become familiar with the details and reasons why the tests are necessary for flooring work. Some inexperienced individuals try to use a pin moisture meter for concrete floor testing rather than following the rigorous ASTM standard.
While a pin or even pinless moisture meter can give a general idea of the presence of moisture, their results do not provide information upon which to make sound decisions.
To explain why the ASTM-F-2170 standard is so necessary in the world of concrete and flooring work, it’s necessary to know what the standard is.
What ASTM-F-2170 is, and Why Contractors Follow it
The ASTM-F-2170 standard is a testing method for determining the relative humidity (RH) that is present in concrete floor slabs. This testing method was developed by the American Society for Testing and Materials, aka ASTM International.
Using this testing method, contractors are better able to predict how a concrete slab will behave in its final use. This helps prevent contractors from building on concrete subfloors that aren’t yet ready.
Building on concrete that isn’t ready can lead to flooring problems such as buckling, warping, or other moisture-related problems as excess moisture from the concrete bleeds into the flooring installed over it.
Worse yet, these issues lead to callbacks and dissatisfied customers, which can hurt a contractor’s business. By following the ASTM-F-2170 testing method, flooring contractors can avoid these problems from poorly prepared concrete.
Beyond that, contractors follow this ASTM testing standard because it is often considered the gold standard for moisture testing in concrete, and many manufacturers cite it as an accepted testing method. If a contractor doesn’t follow this testing guideline, or any other manufacturer-approved testing method, the manufacturer may deem their product warranty is voided and not assume responsibility if there’s a flooring failure later because of moisture issues.
How In-Situ Probes Figure into the Test
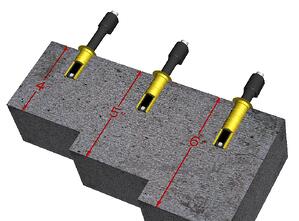
Under this testing standard, contractors drill holes in a concrete floor and insert sleeves that are then sealed. After this is done, the holes are given time to acclimate so that any changes caused by drilling a hole into the concrete can be eliminated.
These in-situ probes that are left in the concrete are then attached to an RH meter (also known as a thermo-hygrometer) to take readings of the moisture conditions deep in the slab.
The readings are taken on a regular basis until the RH conditions in the concrete indicate that it’s ready.
Following the Standard
To adhere to the ASTM-F-2170 standard, several steps need to be taken:
First, the contractor needs to verify the slab’s thickness and surface area, as well as the RH of the room/area where the concrete slab is located, and any potential sources of moisture that may be present.
Knowing the depth of the slab lets you know how deep to drill the testing holes, and knowing the total surface area tells you how many test sites you’ll need to meet the standard’s minimum requirements.
Checking the RH of the area where the concrete slab is located and identifying possible moisture intrusion sources can help you see why a slab might not be ready for the next step.
Additionally, no in-situ probe should be left in concrete for more than 30 days without a calibration check, according to the standard. This is because concrete is a mildly caustic environment, which can damage RH sensors, causing them to lose calibration and start to return unreliable readings.
Overall, the use of the concrete testing ASTM-F-2170 standard is a key part of any flooring job. Following the standard can help reduce callbacks, improve the useful life of flooring, and preserve a contractor’s reputation through superior quality work.

Comments